Bizarre Mars photo changes how we think about the planet’s watery past
Exploration of Mars has revealed some strange but naturally occurring shapes.
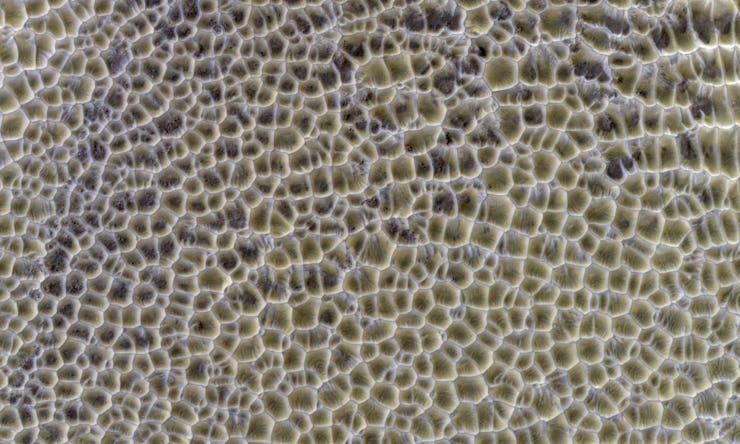
In our exploration of Mars, we’ve seen some strange but naturally occurring shapes. Polygons — a shape with at least three straight sides and angles, typically with five or more — have been seen in several different Martian landscapes.
Scientists say these shapes are of great interest because they often indicate the presence of shallow ice, or that water formerly was present in these areas.
For example, the Phoenix lander saw polygon shapes on the ground in the Mars Arctic region, and these shapes were produced by seasonal expansion and contraction of ground ice. The HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has found large polygon-shaped ridges and networks of giant polygonal troughs created by ancient lakes that have evaporated.
But HiRISE (the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) has also seen these odd shapes within dry, dusty sand dunes. In our lead image, these polygon-shaped sand dunes have an almost honeycomb-like appearance.
“Polygons form by the intersecting ridges of sand dunes,” the HiRISE team explained on their website. “If this deposit were to become indurated and eroded, we might not be able to tell that they originated as wind-blown dunes, and interpret the polygons as evidence for a dried-up lake, for example.”
The HiRISE team says the dune field seen above is about one kilometer (0.62 miles) across.
But could there be a connection between these strange-shaped dunes and water? These types of dunes often accumulate in the bottoms of craters, which is also a good setting for an ancient or temporary lake.
The image below is from HiRISE, showing Victoria Crater on Mars (where the Opportunity rover explored), showing a crisscrossing, polygon-shaped dune field:
Victoria Crater as seen by HiRISE.
But there are quite different conditions on Mars that form dunes, as opposed to how they form on Earth. So, I guess we’ll have to keep exploring Mars to find the answer!
This article was originally published on Universe Today by Nancy Atkinson. Read the original article here.
This article was originally published on